
Are you a right brain thinker or do you use your left brain? Which do you think makes you a better leader? My book club is currently reading Daniel H. Pink’s book, “A Whole New Mind”. The book explores the strengths and skills of leadership from the perspective of left and right brain skills. It looks at what was needed in the past to be a successful leader and what is needed now. To date, our leaders have leaned towards left-brain thinkers. MBAs and lawyers who could crunch numbers and construct contracts, but he argues that the time is right for new kind of leader. Those of a more creative bend, those capable of recognizing patterns, telling stories and a generally more inventive frame of mind.
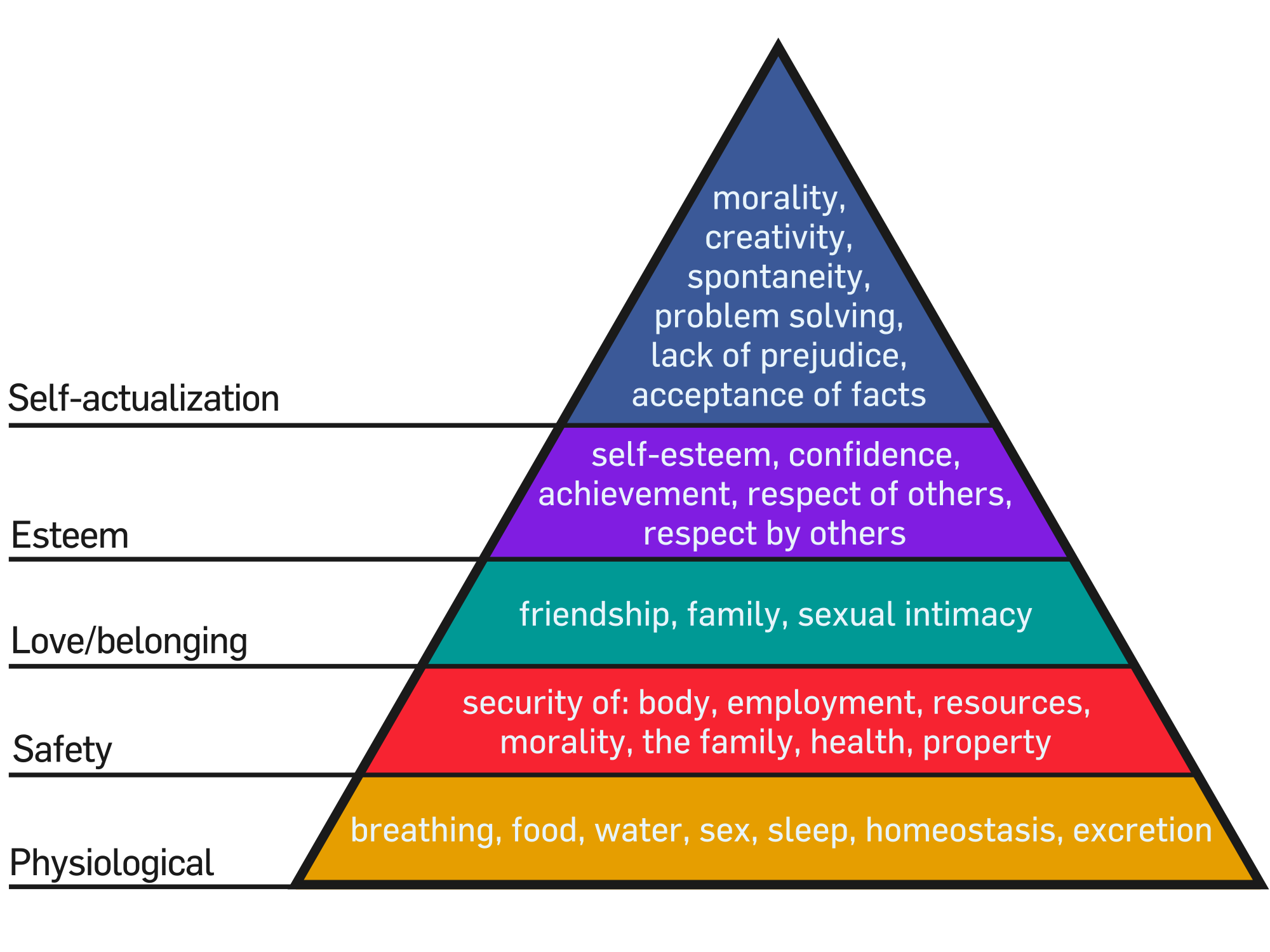
Pink suggests that in times of abundance humans begin to look for more meaningful ways of defining success. The basic premise is that that if you are living in a time of abundance (which many of us are in North America and Europe) then you start to wonder about different things. You start to aspire to achieve more emotionally complex goals. In essence, you move up Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to focus on self-actualization and start to think about other, more emotionally charged means of reaching satisfaction, success or happiness…depends on your personal target.
 I might have scoffed at that thinking a little, but I just spent the last two weeks reading a variety of blogs about finding happiness, managing emotional vampires and getting past the “aaaarrgggghhh” moments in our lives. It seems Daniel Pink might have a point about where we are in our economic and emotional development. Our definition of what defines success seems to have become more complex. Simply having a job or even achieving monetary success is no longer enough. We need to have a deep-rooted satisfaction with the work we do. The blossoming blogosphere, the emergence of countless freelancers, our praise of entrepreneurial spirit, our insistence on visionary leadership and an emerging interest in working from home all speak to a desire to lead more independent and satisfying lives. We’re looking for control and to be part of something better.
I might have scoffed at that thinking a little, but I just spent the last two weeks reading a variety of blogs about finding happiness, managing emotional vampires and getting past the “aaaarrgggghhh” moments in our lives. It seems Daniel Pink might have a point about where we are in our economic and emotional development. Our definition of what defines success seems to have become more complex. Simply having a job or even achieving monetary success is no longer enough. We need to have a deep-rooted satisfaction with the work we do. The blossoming blogosphere, the emergence of countless freelancers, our praise of entrepreneurial spirit, our insistence on visionary leadership and an emerging interest in working from home all speak to a desire to lead more independent and satisfying lives. We’re looking for control and to be part of something better.
Could Daniel Pink be right about which side of the brain will make for a more effective leader in today’s environment? Do we need bosses who know how to be responsive to our more complex emotional demands? Leaders, who can think outside of the box, be holistic and intuitive because not only is it what workers are looking for, but may also be what the work we do increasingly requires.
The use of automation and less costly workers means that jobs in the first world are more complex and require a different level of thinking. Couple that with our preoccupation with self-actualization and it makes sense that we need a different kind of leader…or does it?
In discussion with Jen Hunter, a management expert and facilitator she responded in this way when asked what her thoughts were, “Would you go to the gym and only exercise one side of your body? Unlikely, so why would you want leaders who only used one side of their brain? It doesn’t matter which half, it matters that they only use half.”
That assessment makes sense to me, but beyond that comes the big elephant in the room, the brain function itself. While we often hear about the two sides of the brain as having distinctly different functions, they are not quite that easily defined. Much more research is still required. So for the sake of this conversation lets simply consider that the skills we have traditionally seen as strengths for our leaders may be changing.
What do you think? Do you think we need more right brain leadership? Do left-brain thinkers still make for better leaders? Is the whole conversation of what drives us even relevant? Are we solving more complex problems in our jobs? Are we aspiring to more complex goals?
Want to test which side you use? Follow the 3rd link to, “Instant Personality Test”, it’s quick though I can’t speak to its accuracy.
Related articles
- I’m Daniel Pink, and This Is How I Work (lifehacker.com)
- [Science Solitaire] Which brain side are you on? (rappler.com)
- Instant Personality Self Test : Your brain thinks mostly left / right / both? (propelsteps.wordpress.com)



